The Evil Black Economist releases the 2016 Economic State of Black America report. The report is dedicated to Martin Luther King. The report is grouped into four sections: Wealth, Income,
Health, and Happiness
This
project grew out of a discussion over how to measure the impact of the Presidency
of Barack Obama. President Obama is widely viewed as have a very successful presidency in terms of accomplishments and popularity. However his success was affected by two larger issues: the 2007
recession and 35 years of a shrinking middle class. He did have one major accomplishment and a slew of minor successes. His major legacy is improving health care access for 20 million who previously were uninsured.
Summary
Overall, Black Americans, like many in the US, are not doing well. The 2007 recession and financial crisis led to a huge number of foreclosures wiping out a huge amount of Black wealth. Jobs remain scarce. As of 2016 has Black unemployment has recovered to 2007 levels.. The Black unemployment rate of 7.8% is the same or below the 2007 rate. Black people have lost 10 years of income and wealth.
There is some good news. Incomes are slowly rising. More Blacks are participating in the labor force while White Men drop out. Blacks tend to work in Service and Transportation jobs. Black business ownership was flat in the latest survey.
Living in Poverty was report by 26% of Blacks. One in five (21.5%) Black households worries about food and 26% collect food stamps.
Educationally, we graduate high school at almost the same rate as Whites but attend college at a lower rate (10% difference). We graduate from college at an even lower rate(20% difference) as compared to Whites. Black student debt is estimated at twice that of Whites.
White economic indicators are trending flat or down, social and health indicators are moving in the right direction. Life expectancy has increased while infant mortality has decreased. Health insurance coverage is up and crime has dropped.
Finally, the measures of economic opportunity do not look good. By one estimate, a Black poor child has only a 4% chance of being a rich adult and a 50% chance of remaining a poor adult.
Finally, if you have a Black statistic you would like added to the report, please send and e-mail to:
evilblackeconomist@gmail.com
Thanks
======================================================================
Summary
Overall, Black Americans, like many in the US, are not doing well. The 2007 recession and financial crisis led to a huge number of foreclosures wiping out a huge amount of Black wealth. Jobs remain scarce. As of 2016 has Black unemployment has recovered to 2007 levels.. The Black unemployment rate of 7.8% is the same or below the 2007 rate. Black people have lost 10 years of income and wealth.
There is some good news. Incomes are slowly rising. More Blacks are participating in the labor force while White Men drop out. Blacks tend to work in Service and Transportation jobs. Black business ownership was flat in the latest survey.
Living in Poverty was report by 26% of Blacks. One in five (21.5%) Black households worries about food and 26% collect food stamps.
Educationally, we graduate high school at almost the same rate as Whites but attend college at a lower rate (10% difference). We graduate from college at an even lower rate(20% difference) as compared to Whites. Black student debt is estimated at twice that of Whites.
White economic indicators are trending flat or down, social and health indicators are moving in the right direction. Life expectancy has increased while infant mortality has decreased. Health insurance coverage is up and crime has dropped.
Finally, the measures of economic opportunity do not look good. By one estimate, a Black poor child has only a 4% chance of being a rich adult and a 50% chance of remaining a poor adult.
Finally, if you have a Black statistic you would like added to the report, please send and e-mail to:
evilblackeconomist@gmail.com
Thanks
======================================================================
Wealth / Home Ownership / Housing Statistics
Net Worth
Net worth is the most basic measure of wealth. It is the value of assets a household controls. Middle class people in the US usually have one large asset: their home. The rich have multiple real estate properties and investment assets. The poor have no assets at all.
The table below lists household assets from the Federal Reserve's Survey of Consumer Finances. The median (one-half above and one-half below) is a better measure of assets because people like Oprah and Bob Johnson (BET) skew the average number.
The ratio of Black wealth to White wealth was 12/100 meaning Blacks has just 12% of the assets of Whites and Whites were 8 times richer than Blacks.
The ratio of Black wealth to White wealth was 12/100 meaning Blacks has just 12% of the assets of Whites and Whites were 8 times richer than Blacks.
| 2013 Median | 2013 Mean | Median Ratio to White | |
|---|---|---|---|
| White | $139,857 | $572,870 | 100% |
| Black | 17,387 | 101,736 | 12.4% |
| Hispanic/Latino | 15,758 | 126,808 | 11.3% |
| Other | 84,284 | 460,960 | 60.3% |
Here is the trend over the past 12 years. Black home ownership took a huge hit during the last recession.
Source: Federal Reserve Survey of Consumer Finance, 2013
Home Ownership
| 2011 | 2013 | 2015 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 114,907 | 115,852 | 118,290 |
| White | 92,820 | 93,284 | 93,760 |
| Black | 14,694 | 15,015 | 15,998 |
| Hispanic/Latino | 13,841 | 14,675 | 15,617 |
| Asian | 4,620 | 4,725 | 5,477 |
Source:
US Census, American Housing Survey
| 4Q 2016 Rate | |
|---|---|
| Total | 63.7% |
| White | 72.2% |
| Black | 41.7% |
| Hispanic/Latino | 46.3% |
| Other | 53.7% |
Chart of US home ownership rates over time period 2013 to 2016.
Source: US Census, Quarterly Residential Vacancies and Home Ownership, Q4 2016. Note: 4Q 2016 was released as we went to press.
Mortgage Loans
Mortgage Loans
The primary way people build assets in the US is through home ownership. And the main way to buy a home is with a mortgage loan. However, the mortgage loan market has under gone a huge crisis. In the 2000's the "sub-prime" mortgage market was developed and in the 2007 it collapsed. Now we are in a slow recovery from that event.
The majority of Black mortgages are non-conventional mortgages.
Black 2013 Mortgage Loan Applications 186,074/ Originated 113,723
The majority of Black mortgages are non-conventional mortgages.
Black 2013 Mortgage Loan Applications 186,074/ Originated 113,723
Black
2014 Mortgage Loan Applications 206,182 / Originated 130,176
We continue to see lower rates of loans made to Black applicants. Also, a higher percentage of the loan are non-conventional loans when compared to Whites.
We continue to see lower rates of loans made to Black applicants. Also, a higher percentage of the loan are non-conventional loans when compared to Whites.
Source:
2016 State of Housing in Black American. NAREB.
www.nareb.com/site-files/uploads/2016/08/NAREB-SHIBA-REPORT-2016-final.pdf
Income
Black / White 2016 Ratio 80%
Black households have a median (half above and half below) income of about earn about $37,000 dollars.
Median Weekly Earnings
| 2015 | 2016 | |
|---|---|---|
| White | $847 | $881 |
| Black | $643 | $675 |
| Hispanic | $624 | $646 |
| Asian | $1,022 | $1,092 |
Black / White 2016 Ratio 80%
Black Men / White Men 2016 Ratio 78%
Black Women / White Women 2016 Ratio 84%
Here is a chart of median weekly earnings for the period 2000-2016.

Here is a chart of median weekly earnings for the period 2000-2016.

Source: BLS, 2016, Median Usual Weekly Earnings from CPS
Household Income
Household Income
Black households have a median (half above and half below) income of about earn about $37,000 dollars.
Median Household Income
| 2014 | 2015 | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|
| White | $56,931 | $60,109 | 5.6% |
| Black | $35,439 | $36,898 | 4.1% |
| Hispanic | $42,540 | $45,148 | 6.1% |
| Asian | $74,382 | $77,166 | 3.7% |
Below is a graph of the trend since 1972.
Source: US Census, Table 1, Income and Earnings Summary Measures by Selected Characteristics: 2014 and 2015
Total Income for Population
One common question is: "How much money do Black people in the US earn collectively?" Well, there are two different measures: one is income and the other is called "Total Money Income (TMI)" which includes transfer payments. In 2015, we earned $610 Billion in income and had a TMI of $898 billion.
The figure for Black Alone or in Combination is even larger at $949 Billion. Black AOIC includes Black people and mixed race and Hispanic people who identify as Black.
One common question is: "How much money do Black people in the US earn collectively?" Well, there are two different measures: one is income and the other is called "Total Money Income (TMI)" which includes transfer payments. In 2015, we earned $610 Billion in income and had a TMI of $898 billion.
The figure for Black Alone or in Combination is even larger at $949 Billion. Black AOIC includes Black people and mixed race and Hispanic people who identify as Black.
| Pop. 2014 | 2014 Income |
Pop. 2015 | 2015 Income |
Total Change |
Pop. Change | Real Income Change | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total |
|
|
|
|
|
0.99% | 5.26% | |||||
| White |
|
|
|
|
|
0.26% | 4.36% | |||||
| Black |
|
|
|
|
|
0.62% | 4.14% | |||||
| Asian |
|
|
|
|
|
4.77% | 3.92% | |||||
| Hisp./Latino |
|
|
|
|
|
2.63% | 6.29% |
| Pop. 2014 | 2014 Income |
Pop. 2015 | 2015 Income |
Total Change |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total |
|
|
|
$9,972,791,397 |
|
||||||
| White |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
| Black AOIC |
|
|
|
|
6.81% | ||||||
| Black Alone |
|
|
|
|
6.63% | ||||||
| Asian |
|
|
|
|
13.07% | ||||||
| Hisp./Latino |
|
|
|
|
13.35% |
Occupations
Where do Black people work ?
Blacks are underrepresented in Management, Business, Science and the Arts(MBSA) and in Natural Resources and Farming, Construction and Maintenance(NRCM). They are over represented in Services and Transportation.
Key:
PTMM - Production, Transportation and Material Management
| Occupation | Total | % | Male | % | Female | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Total | 150,534,773 | 100% | 79,120,041 | 100% | 71,414,732 | 100% |
| MBSA | --- | 37.1% | --- | 33.5% | --- | 44.1% | |
| Services | --- | 18.0% | --- | 14.8% | --- | 21.5% | |
| Sales & Office | --- | 23.6% | --- | 17.1% | --- | 30.8% | |
| NRCM | --- | 9.0% | --- | 31.1% | --- | 0.9% | |
| PTMM | --- | 12.3% | --- | 31.1% | --- | 5.8% | |
| White | Total | 112,857,159 | 100% | 60,181,754 | --- | 52,675,405 | --- |
| MBSA | --- | 35.2% | --- | 33.5% | --- | 43.1% | |
| Services | --- | 43.1% | --- | 13.2% | --- | 19.5% | |
| Sales & Office | --- | 23.8% | --- | 17.1% | --- | 31.3% | |
| NRCM | --- | 9.6% | --- | 17.2% | --- | 0.9% | |
| PTMM | --- | 11.6% | --- | 17.3% | --- | 5.1% | |
| Black | Total | 17,198,924 | 100% | 7,885,268 | 100% | 9,313,656 | 100% |
| MBSA | --- | 28.7% | --- | 22.8% | --- | 33.6% | |
| Services | --- | 25.0% | --- | 22.0% | --- | 27.5% | |
| Sales & Office | --- | 25.2% | --- | 18.7% | --- | 30.8% | |
| NRCM | --- | 5.1% | --- | 10.5% | --- | 0.6% | |
| PTMM | --- | 16.0% | --- | 26.0% | --- | 7.5% | |
| Hispanic / Latino | Total | 24,845,756 | 100% | 14,055,426 | 100% | 10,790,330 | 100% |
| MBSA | --- | 20.5% | --- | 16.5% | --- | 25.7% | |
| Services | --- | 25.6% | --- | 21.1% | --- | 31.5% | |
| Sales & Office | --- | 21.9% | --- | 14.7% | --- | 31.3% | |
| NRCM | --- | 15.6% | --- | 26.1% | --- | 2.0% | |
| PTMM | --- | 16.3% | --- | 21.6% | --- | 9.5% | |
| Asian | Total | 8,633,703 | 100% | 4,504,912 | 100% | 4,128,791 | 100% |
| MBSA | --- | 51.0% | --- | 52.1% | --- | 49.8% | |
| Services | --- | 16.7% | --- | 13.6% | --- | 20.2% | |
| Sales & Office | --- | 19.8% | --- | 16.7% | --- | 23.2% | |
| NRCM | --- | 2.9% | --- | 5.3% | --- | 0.4% | |
| PTMM | --- | 9.6% | --- | 12.4% | --- | 6.5% |
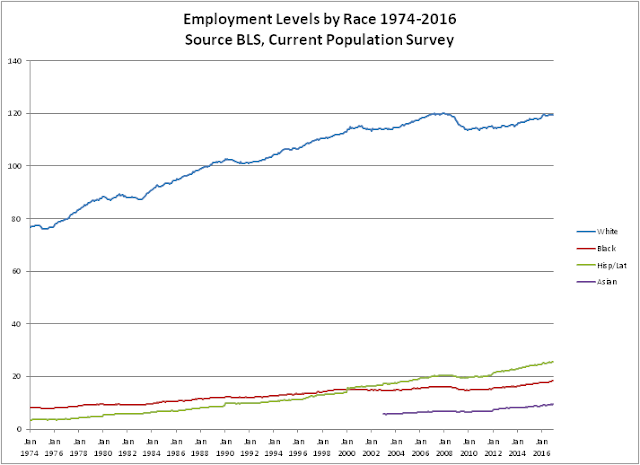
Total Employment Levels
Black employment continues to grow while White employment is decreasing.
Black Employment 2016 18,292,000 people
Black Employment 2015 17,802,000 An increase of 490,000 people
Table Black Unemployment 7.8%
Black Men 7.6% (8.7% 2015)
Black Women 6.8% (7.1% 2015)
Black Teenagers 25.7%
The Black unemployment rate has traditionally been twice the White rate. The Black unemployment rate of 7.8% is the lowest since August 2007.
Labor Force Participation
The Black labor market participation rate has trended upward in the past year to 62.4% from a low of 60.3% in 2013. Blacks are returning to work as Whites drop out.
Source: BLS, January Labor Report and website
Business Ownership and Formation
Black business ownership has been flat while White owners have decreased and Hispanic and Asian business owners have increased.
Poverty
People in Poverty
| 2014 | % of Total Population |
2015 | % of Total Population |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 46,657,000 | 14.8% | 43,123,000 | 13.5% |
| White | 19,652,000 | 10.1% | 17,786,000 | 9.1% |
| Black | 10,755,000 | 26.2% | 10,020,000 | 24.1% |
| Hispanic/Latino | 13,104,000 | 23.6% | 12,133,000 | 21.4% |
| Asian | 2,137,000 | 12.0% | 2,078,000 | 11.4% |
Source: US Census, Income and Poverty in the US, 2015
Child Poverty (18 and Under)
Child Poverty (18 and Under)
| 2014 | % of Total Population |
2015 | % of Total Population |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 15,540,000 | 21.1% | 14,509,000 | 19.7% |
| White | 9,602,000 | 17.9% | 9,204,000 | 17.2% |
| Black | 4,090,000 | 37.1% | 3,651,000 | 32.9% |
| Hispanic/Latino | 5,745,000 | 31.9% | 5,269,000 | 28.9% |
| Asian | 524,000 | 14.0% | 466,000 | 12.3% |
Source:
US Census, Income and Poverty in the US, 2015
Food Security by Household 2015
Food security is defined at three levels: 1) food secure, 2) low food security and 3) very low food security. Food secure is defined as "access at all times to enough food for an active, healthy
life for all household members." People who are food insecure do not meet condition one. They have either low food or very low food security. Very low food security is defined as "one or more household members had reduced eating patterns and their eating patterns were disrupted at times during the year because the household lacked money and other resources for food."
| Race | Total | Food Secure | % | Insecure Total |
Insecure % |
Low | Low % | Very Low | Very Low % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 83,931 | 75,563 | 90.0% | 8,368 | 10.0% | 4,759 | 5.7% | 3,609 | 4.3% |
| Black | 15,734 | 12,357 | 78.5 | 3,377 | 21.5 | 2,127 | 13.6 | 1,250 | 7.9 |
| Hispanic | 16,803 | 13,592 | 80.9 | 3,211 | 19.1 | 2,132 | 12.7 | 1,079 | 6.4 |
| Other | 8,695 | 7,803 | 89.7 | 892 | 10.3 | 521 | 6.0 | 371 | 4.3 |
Source: Household Food Security in the United States 2015, www.ers.usda.gov/webdocs/publications/err215/err-215.pdf
Food Stamps (Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program)
About 5.7 million Black households receive food stamps in 2015.
| 2015 | Total (000) | % | Children | % | Elderly | % | Disabled | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 22,293 | 100% | 9,510 | 100% | 4,361 | 100% | 4,498 | 100% |
| White | 8,757 | 39.3% | 3,092 | 32.5% | 1,857 | 42.6% | 2,047 | 45.5% |
| Black | 5,747 | 25.8% | 2,335 | 24.5 | 915 | 21.0% | 1,271 | 28.3% |
| Hispanic/Latino | 2,538 | 11.4% | 1,133 | 11.9 | 575 | 13.2% | 347 | 7.7% |
| Asian | 561 | 2.5% | 194 | 2.0 | 250 | 5.7% | 38 | 0.9% |
Individual Food Stamps Participants
Eleven million Black people participate in the food stamp program.
| 2015 | Total(000) | % | Female(000) | % | Male(000) | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 45,184 | 100% | 25,637 | 56.7 | 19,547 | 43.3 |
| White | 16,574 | 36.7% | 9,405 | 20.8% | 7,170 | 15.9% |
| Black | 11,772 | 26.1% | 6,846 | 15.2 | 4,926 | 10.9% |
| Hispanic/Latino | 7,730 | 17.1% | 4,336 | 9.6 | 3,394 | 7.5% |
| Asian | 1,301 | 2.9% | 716 | 1.6 | 585 | 1.3% |
Children Raised by Single Parents (in 000)
Black
Kids (18 old and under) Total 11,101
Black
Kids (18 old and under) Living with both parents 4,294
Black
Kids (18 old and under) Living with Mother 5,722
Black
Kids (18 old and under) Living with Father 439
Black
Kids (18 old and under) Living with Single Parent 55%
White 19%
Asian 13%
Hispanic
29%
Source: US
Census, Families and Living Arrangements October 2016
Education
Educational Attainment
| 2015 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Pop. 18 and older | High School or Higher | % of Pop. | Bachelors or Higher | % of Pop. | |
| Total | 242,831,196 | 210,098,654 | 86.5% | 66,036,180 | 27.2% |
| White | 161,426,754 | 143,105,261 | 88.7% | 50,142,764 | 31.1% |
| Black | 24,689,835 | 20,678,704 | 83.8% | 4,812,215 | 19.5% |
| Hisp./Latino | 29,952,299 | 19,439,898 | 64.9% | 4,275,337 | 14.3% |
| Asian | 11,220,496 | 9,647,290 | 86.0% | 5,770,522 | 51.4% |
Source: 2015 American Community Survey
Graduation Rate from 4-year program
Black 6 year or less college graduation rate (2008-2014) 40.9%
Black 6 year or less college graduation rate (2008-2014) 40.9%
Black
Male 35.3%
Black
Female 44.8%
=======================================
=======================================
White 63%
Black 41%
Hispanic 53%
Asian 71%
Source DOE: National Center for Educational Statistics, Postsecondary Graduation Rate, 2014, Table 326.10
Note: Cohorts are from 1996 to 2007.
High School
Graduation Rate
| Race | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 90.8% | 91.2% | 91.7% |
| White | 95.6 | 95.4 | 95.2 |
| Black | 91.9 | 92.5 | 91.1 |
| Hispanic/Latino | 74.7 | 77.1 | 80.6 |
| Asian | 96.6 | 95.8 | 96.8 |

Source Department of Education: National Center for Educational Statistics, Postsecondary Graduation Rate, 2014, Table 104.20
College and Graduate Student
Debt
Black college students have about $7,300 dollars in extra debt compared to White college students and $24,000 more 4 years later.
Black college students have about $7,300 dollars in extra debt compared to White college students and $24,000 more 4 years later.
2012
|
Under Graduate
Borrowing
|
Total Owed
4 years Later
|
|---|---|---|
| Total | $16,491 | --- |
| White | $16,046 | $28,006 |
| Black | 23,421 | 52,726 |
| Hispanic/Latino | 15,663 | 29,949 |
| Asian | 11,935 | 26,253 |
Note: The US Department of Education does not collect statistics on total debt by race. Brookings has estimated the amounts.
Source: https://www.brookings.edu/research/black-white-disparity-in-student-loan-debt-more-than-triples-after-graduation/, Oct, 2016 Report(2012 Data)
Infant Mortality
The Black infant mortality rate is 11.11 per every one thousands live births.
| Per 1000 Live Births | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 6.39 | 6.14 | 6.07 | 5.98 | 5.98 |
| White | 5.33 | 5.18 | 5.07 | 5.04 | 5.06 |
| Black | 12.40 | 11.46 | 11.45 | 11.19 | 11.11 |
| Hispanic/Latino | 5.29 | 5.25 | 5.15 | 5.11 | 5.00 |
| Asian | 4.40 | 4.27 | 4.36 | 4.06 | 4.07 |
Source: National Vital Statistics Report
https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr64/nvsr64_09.pdf
Life Expectancy
Black men have a life expectancy of 72.3 years while Black women have a life expectancy of 78.4 years.
| In Years | 2013 | 2014 |
|---|---|---|
| Total | 78.8 | 78.8 |
| White | 78.9 | 78.8 |
| Black | 75.1 | 75.2 |
| Hispanic/Latino | 81.6 | 81.8 |
Source: CDC National Vital Statistics Reports https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr65/nvsr65_08.pdf
Teenage Birth Rate(15-19)
The teenage birth is measured per 1000 live births. Black teenagers age 15-19 had a birth rate of about 32 per 1000 which is almost of half of the 2006 rate. The drop was -73% over the 10 year period.
| Per 1000 Live Births | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 41.1 | 41.5 | 40.2 | 37.9 | 34.2 | 31.3 | 29.4 | 26.5 | 24.2 | 22.3 |
| White | 26.7 | 27.2 | 26.7 | 25.7 | 23.5 | 21.7 | 20.5 | 18.6 | 17.3 | 16.0 |
| Black | 61.9 | 62.0 | 60.4 | 56.8 | 51.5 | 47.3 | 43.9 | 39.0 | 34.9 | 31.8 |
| Hispanic/Latino | 77.4 | 75.3 | 70.3 | 63.6 | 55.7 | 49.6 | 46.3 | 41.7 | 38.0 | 34.9 |
| Asian | 15.3 | 14.8 | 13.8 | 12.6 | 10.9 | 10.2 | 9.7 | 8.7 | 7.7 | 6.9 |
Source: National Center for Health Statistics, NCHS Data Brief No. 264, November 2016 and https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/databriefs/db259.pdf
Unmarried Birthrate
Seventy-One(71) percent of all Black children are born to unmarried women.
Percentage of Births to Unmarried Women
| Percent of Live Births | 2015 |
|---|---|
| Total | 40.3% |
| White | 40.4 |
| Non-Hispanic White | 29.2 |
| Black | 70.1 |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 70.6 |
| Hispanic/Latino | 53.0 |
| Asian | 16.4 |
Birth Rates for Unmarried Women
| Per 1000 Live Births | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 47.2 | 50.3 | 51.8 | 51.8 | 49.9 | 47.5 | 46.0 | 45.3 | 44.3 | 43.9 |
| White | 30.4 | 32.4 | 33.8 | 34.3 | 33.6 | 32.9 | 32.3 | 32.1 | 31.7 | 31.8 |
| Black | 67.2 | 70.7 | 71.4 | 71.0 | 68.7 | 65.3 | 63.7 | 62.6 | 61.7 | 61.5 |
| Hispanic/Latino | 96.2 | 101.5 | 102.1 | 97.3 | 89.4 | 80.6 | 75.1 | 72.6 | 69.9 | 68.5 |
| Asian/Pac. Isl. | 22.8 | 23.4 | 23.9 | 23.9 | 23.6 | 22.3 | 22.4 | 22.9 | 21.8 | 21.7 |
Source: National Vital Statistics Reports, Vol. 64, No. 12, December 23, 2015
Health Insurance Coverage
Close to 90% of all people have health insurance including 88% of Black people. Health insurance is either private or government funded.
| Pop.2014 | Insured | % | Uninsured | % | Pop.2015 | Insured | % | Uninsured | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 316,168 | 283,200 | 89.6% | 32,968 | 10.4% | 318,868 | 289,903 | 90.9% | 28,966 | 9.1% |
| White | 195,352 | 180,528 | 92.4% | 14,824 | 7.6% | 195,646 | 182,546 | 93.3% | 13,100 | 6.7% |
| Black | 41,226 | 36,380 | 88.3% | 4,847 | 11.8% | 41,703 | 37,076 | 88.9% | 4,627 | 11.1% |
| Hisp/Lat | 55,614 | 44,556 | 80.1% | 11,059 | 19.9% | 56,873 | 47,637 | 83.8% | 9,235 | 16.2% |
| Asian | 17,796 | 16,137 | 90.7% | 1,659 | 9.3% | 18,249 | 16,889 | 92.6% | 1,360 | 7.4% |
Source: US Census, Health Insurance Coverage in the United States: 2015
Crime
Arrest data for key crime categories. Some categories were combined to save space.
| Arrests | Total | White | % | Black | % | Hispanic | % | Asian | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 8,248,709 | 5,753,212 | 69.7% | 2,197,140 | 26.6% | 1,204,862 | 18.4% | 101,064 | 1.2% |
| Murder/Manslaughter | 8,508 | 3,908 | 45.9% | 4,347 | 51.1% | 1,370 | 20.8% | 126 | 1.5% |
| Rape | 17,370 | 11,809 | 68.0% | 4,907 | 28.2% | 3,516 | 26.8% | 271 | 1.6% |
| Assault | 287,566 | 184,024 | 64.0% | 92,237 | 32.1% | 59,883 | 24.6% | 4,631 | 1.6% |
| RBLT | 1,192,211 | 807,016 | 89.6% | 350,180 | 10.4% | 158,870 | 16.7% | 14,472 | 1.2% |
| Violent Crime Total | 386,467 | 232,180 | 60.1% | 140,543 | 36.4% | 77,557 | 23.9% | 5,696 | 1.5% |
| Property Crime Total | 1,125,950 | 779,529 | 69.2% | 312,647 | 27.8% | 146,980 | 16.4% | 13,892 | 1.2% |
| Drug Related | 1,136,950 | 803,809 | 80.1% | 307,140 | 19.9% | 186,841 | 20.3% | 12,436 | 1.1% |
| DUI+Alcohol | 1,340,158 | 1,081,956 | 80.7% | 181,008 | 13.5% | 236,054 | 21.6% | 22,207 | 1.7% |
| Other | 2,455,238 | 1,683,297 | 68.6% | 688,146 | 28.0% | 316,689 | 16.6% | 25,197 | 1.0% |
RBLT is Robbery, Burglary, Larceny, Theft and Motor Vehicle Theft. Drug related is the same as Drug Abuse Violations. DUI plus Alcohol is Driving while under the influence, Liquor Laws and Drunkenness.
Source: FBI Uniform Crime Report, 2015, Arrest by Race and Ethnicity
Incarceration
Black
2014 Jail Population 263,800
Black
2015 Sentenced Prisoners State and Federal 523,000
Black
Incarceration Rate (>18 or older) per 100,000 1745
| Male | Female | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Total | Total Male | White | Black | Hispanic | Other | Total Female | White | Black | Hispanic | Other |
| 2011 | 1,537,415 | 1,433,741 | 465,100 | 555,300 | 331,500 | --- | 103,674 | 51,100 | 26,000 | 18,400 | --- |
| 2012 | 1,511,480 | 1,410,191 | 451,252 | 527,768 | 315,234 | 115,937 | 101,289 | 49,352 | 23,386 | 16,968 | 11,584 |
| 2013 | 1,516,879 | 1,412,745 | 454,100 | 526,000 | 314,600 | 118,100 | 104,134 | 51,500 | 23,100 | 17,600 | 11,900 |
| 2014 | 1,508,636 | 1,402,404 | 453,500 | 516,900 | 308,700 | 123,300 | 106,232 | 53,100 | 22,600 | 17,800 | 12,800 |
| 2015 | 1,476,847 | 1,371,879 | 446,700 | 501,300 | 301,500 | 122,400 | 104,968 | 52,700 | 21,700 | 17,900 | 12,700 |
| Male per 100,000 | Female per 100,000 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Total | Total Male | White | Black | Hispanic | Other | Total Female | White | Black | Hispanic | Other |
| 2011 | 492 | 932 | 478 | 3,023 | 1,238 | --- | 65 | 51 | 129 | 71 | --- |
| 2012 | 480 | 909 | 463 | 2841 | 1158 | 972 | 63 | 49 | 115 | 64 | 90 |
| 2013 | 478 | 904 | 466 | 2791 | 1130 | 998 | 65 | 51 | 113 | 65 | 93 |
| 2014 | 471 | 890 | 465 | 2724 | 1091 | 968 | 65 | 53 | 109 | 64 | 93 |
| 2015 | 458 | 863 | 457 | 2613 | 1043 | 929 | 64 | 52 | 103 | 63 | 90 |
Source Bureau of Justice Statistics
Happiness
Harris Poll Happiness Index by Race
| Race | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2013 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 35 | 35 | 32 | 32 | 34 |
| Black | 35 | 41 | 40 | 44 | 36 |
| Hispanic | 32 | 36 | 39 | 35 | 28 |
Source: Harris Poll Happiness Index, June 2013
http://www.theharrispoll.com/health-and-life/Are_You_Happy__It_May_Depend_on_Age__Race_Ethnicity_and_Other_Factors.html
Social Mobility
Social mobility as measured by generational income levels has been dropping. We want to look at some data published in 2014 by Bhash Mazumder of the Chicago Federal Reserve Bank. He compiled data by race on inter-generational incomes.
He found that White men in the lowest one-fifth (quintile) of income had a 26% change of remaining in the lowest fifth and a 10% chance of moving to the highest fifth(top quintile). Black men from the lowest fifth of income and a 50% chance of remaining in the lowest group and only a 4% chance of making it to the top fifth.
Note: Data is from 1978-86 for parents and 2003-2007 for children. Data analysis was published in 2014.
Source: https://www.chicagofed.org/~/media/publications/economic-perspectives/2014/1q2014-part1-mazumder-pdf.pdf
https://www.brookings.edu/blog/social-mobility-memos/2014/02/27/obamas-post-presidency-tackling-the-social-mobility-challenge-for-black-men/